Admin: Key role permissions
The key functional permissions contained within this tab are listed below:
-
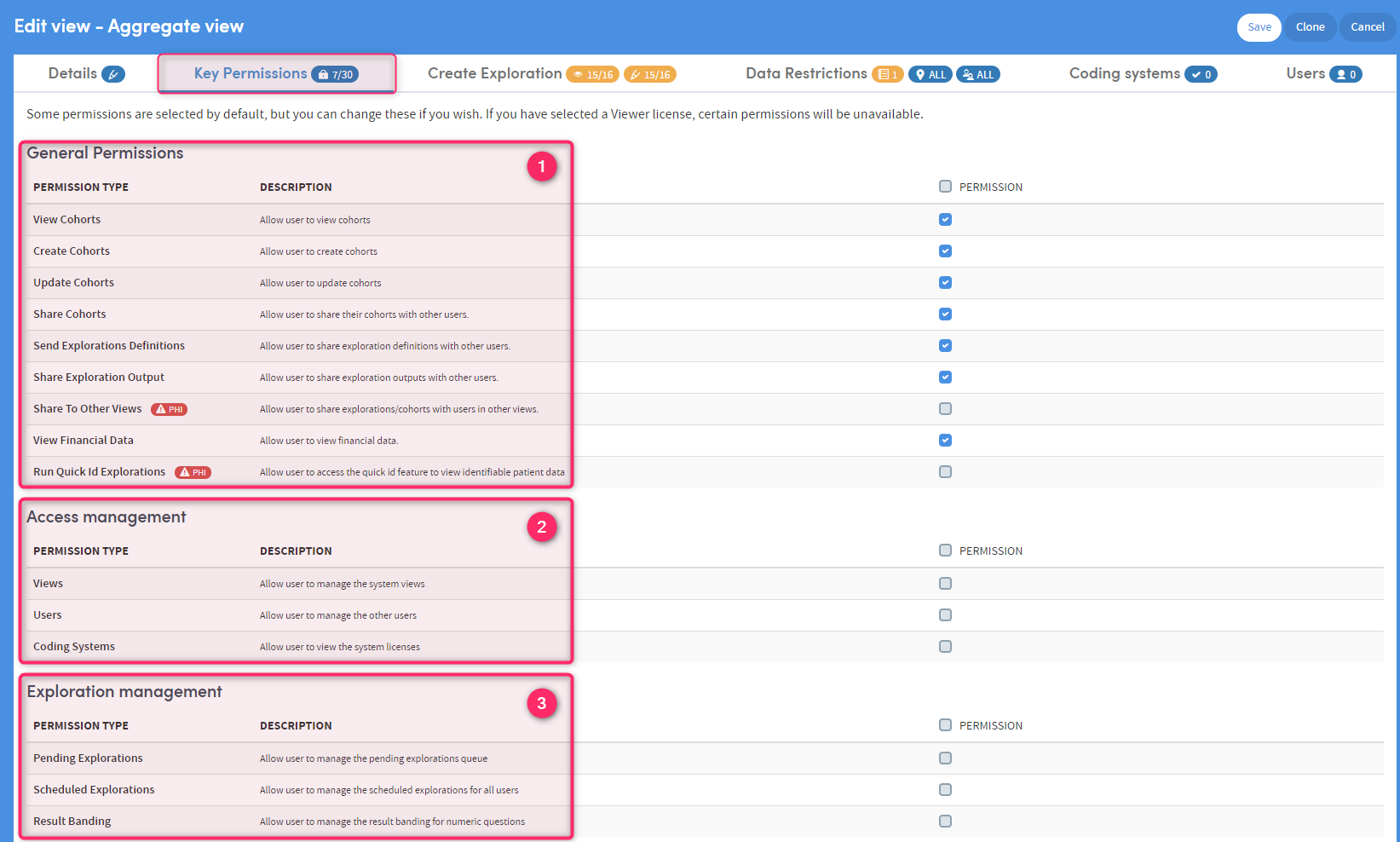
1
General Permissions
This section is for choosing Cohorts and Explorations functions, such as sharing, viewing and creating. This section cab also be used for restricting access to features that will allow users to see data they are not privileged to see.
 Items marked as Protected Health Information (PHI) allow users to view Protected Health Information data or share Protected Health Information data with others. There may also be datasets containing PHI data. These should not be made available to non-PHI roles.
Items marked as Protected Health Information (PHI) allow users to view Protected Health Information data or share Protected Health Information data with others. There may also be datasets containing PHI data. These should not be made available to non-PHI roles.Important: The responsibility for ensuring that PHI permissions are only assigned to roles that should be permitted to view PHI data lies with the user creating the role.
-
2
Access Management
Allows the user to to take on the management of Users and Views, without providing full admin privileges. Ideal for a user who has responsibility for setting up new users of the system.
-
3
Exploration Management
Permits users to view and manage report queues and edit the default result bandings for numeric data items. Once updated, result bandings will default to the new settings in all subsequently created reports and Cohort Insights.
-
4
System Management
Permits users access and privileges to control announcements, cohort insight and insight set management for other users plus configure system settings for all users
-
5
System Monitoring
Allows the user to view key data about the system status, nightly routines, data integrity and audit and system logs.
-
6
Share Exploration Output Options
By default, users can only share report outputs with other users sharing the same role as themselves and, therefore, the same base cohort. This is to prevent the risk of users from other roles receiving and viewing report output data that they should not be permitted to see. However, in some circumstances this is overly restrictive; e.g. it might mean that a junior doctor could not share a worrying finding with his head of department because they had different roles. Hence, the system allows the specification of additional roles that the user can share output data with, over and above their own, as required.
Note: this is potentially overriding other users’ role restrictions and so should be used sparingly, and with care.